See how Collibra supports financial institutions with our industry-leading AI Governance solution.
Collibra AI Governance and OSFI E-23: Navigating Canadian financial regulations

The AI revolution isn't pausing for governance strategies to catch up. It’s especially true for financial services: The industry stands at the precipice of staggering technological transformation. For financial institutions operating in Canada, the regulatory landscape is evolving very quickly, moving AI governance from a "nice-to-have" to a strategic imperative with real consequences.
A primary example is the Government of Canada’s Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI) E-23 guidance for model risk management. What follows is E-23’s purpose and scope:
This Guideline, which is principles-based, sets out OSFI's expectations related to enterprise-wide model risk management (MRM) built on strong model lifecycle principles. It applies to all organizations and to all models, whether they require formal regulatory approval or not.
OSFI expects model risk to be managed on a risk-based and enterprise-wide basis. The term “enterprise” is used throughout this Guideline, when used in a FRPP context, it refers to the contractual arrangements from which the pension plan is derived, and not to the institution represented by the plan sponsor.
Decisions on how to best manage enterprise model risk are the responsibility of the organization.*
What OSFI E-23 ultimately demands is straightforward but profound: OSFI expects organizations to have a good understanding of the model lifecycle including associated processes and controls, as well as a sound and prudent model risk management (MRM) framework.
Beyond compliance: The strategic value proposition
Regulatory compliance might not be the most enjoyable challenge your organization faces. But let's reframe: OSFI E-23 is more than just another compliance hurdle. When viewed as a strategic opportunity, AI leaders can leverage it to position their financial institutions to harness AI's transformative potential while establishing guardrails against the very real risks of unmanaged innovation.
E-23 establishes seven core principles that span everything from lifecycle management to enterprise-wide governance frameworks.
Here are the OSFI E-23 seven principles:
Principle 1: Organizations develop, approve, and implement processes and controls that define expectations for each of the lifecycle components
Principle 2: Processes and controls consider the size, complexity of the organization and the model's usage
Principle 3: Organizations establish an MRM framework that provides an enterprise-wide view of their exposure to model risk
The MRM framework should reflect the organization's risk appetite for model risk and define the process and requirements to identify, assess, manage, monitor, and report on model risk throughout the lifecycle of models employed throughout the organization
Principle 4: Organizations maintain a centralized inventory that is the authoritative record of all models in use and recently decommissioned. The inventory should be evergreen and be subject to robust controls
Principle 5: Organizations have policies, procedures, and governing authorities for each phase of the model lifecycle, where expectations are established based on model complexity and importance
Principle 6: Organizations recognize the interdependency between data and model risk and have adequate policies and procedures to govern data in models. These policies and procedures should align with the organization's data governance framework and strategy at the enterprise level
Principle 7: The model risk rating scheme considers both quantitative and qualitative criteria, as well as impacts to downstream processes
For organizations still treating AI as a technological toy rather than a business transformation engine, E-23 and the principles it promulgates for compliance should serve as a timely wake-up call for forward-thinking financial institutions operating in Canada
The governance fragmentation crisis
For most financial services companies, the problem, however, with complying with E-23 starts with a fundamental structural problem: Your fragmented governance architectures can't scale to meet exponential growth in AI adoption.
This fragmentation surfaces as technological and organizational fault lines that undermine effective oversight, including:
- Data siloed across disparate systems, multiple clouds and on-premises environments
- Critical blind spots in data visibility, context and access controls
- Disconnection between technical and business stakeholders in governance processes
- Inconsistent policy application across increasingly complex data landscapes
As data estates grow more complex and lines of business initiate independent AI initiatives, these governance gaps widen, precisely when the risks of unmanaged AI deployment multiply. The disconnect extends to people as most systems offer no way to bring business users to access data and give it meaning.
The Collibra breakthrough: Unified governance
Collibra AI Governance overcomes these limitations by establishing a unified governance layer independent of underlying technical infrastructure. Our approach fundamentally reframes governance by untethering it from specific systems and sources.
The platform operates through two integrated constructs that provide comprehensive coverage:
- AI use cases: Specific applications of AI trained on particular datasets to solve business problems and deliver measurable value
- AI models: Statistical models that generate predictions, which may serve as components within broader AI use cases
This architecture delivers true unified governance with visibility, context and control throughout the full data cycle—from every producer through every consumer, from input through output.
E-23 purpose and scope
This [OSFI E-23] Guideline, which is principles-based, sets out OSFI's expectations related to enterprise-wide model risk management (MRM) built on strong model lifecycle principles. It applies to all organizations and to all models, whether they require formal regulatory approval or not.OSFI expects model risk to be managed on a risk-based and enterprise-wide basis. The term “enterprise” is used throughout this Guideline, when used in a FRPP context, it refers to the contractual arrangements from which the pension plan is derived, and not to the institution represented by the plan sponsor.
Decisions on how to best manage enterprise model risk are the responsibility of the organization.*
Architecting for OSFI E-23 compliance: The Collibra framework
Here's how Collibra maps directly to the model lifecycle requirements outlined in OSFI E-23:
Rationale for modeling ( E-23 4.1): Purpose-driven development
Collibra AI Governance supports documenting the business purpose, scope and intended use of a model, aligning with OSFI E-23's requirement to clearly articulate why a model is needed and how its outputs will be used. Additionally, Collibra can track stakeholders involved in the AI use case, which could include model users, data offices, compliance and legal departments.
The Collibra Platform ensures models are developed with clear purpose and defined stakeholder accountability—not merely because the technology exists, but because it serves a strategic business objective.
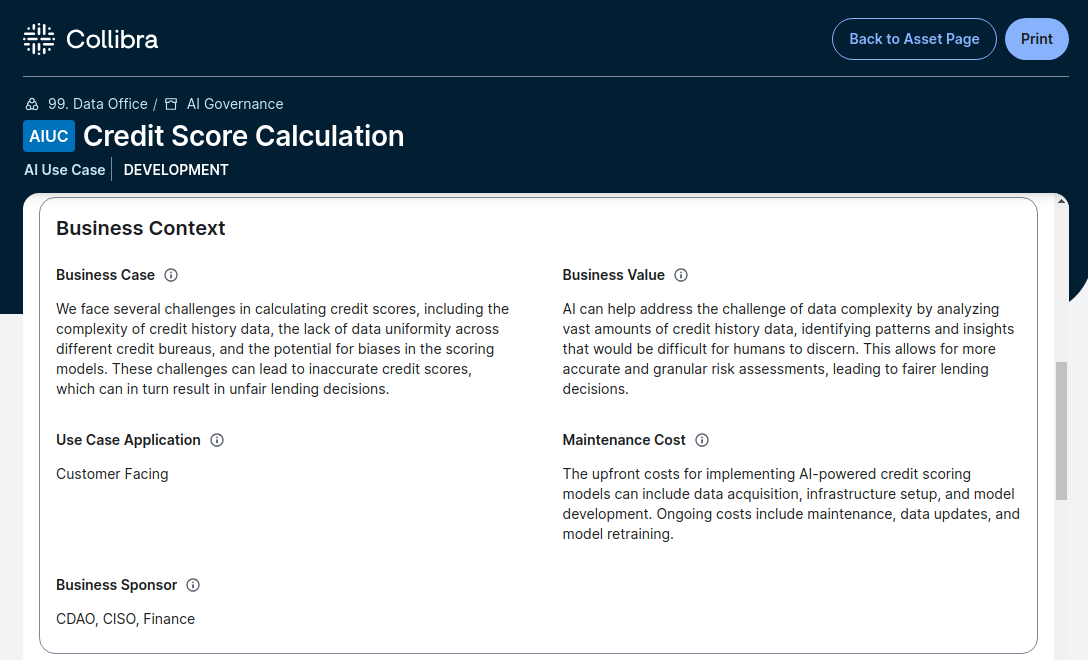
An example screen showing business context as part of an overall Rationale for Modeling.
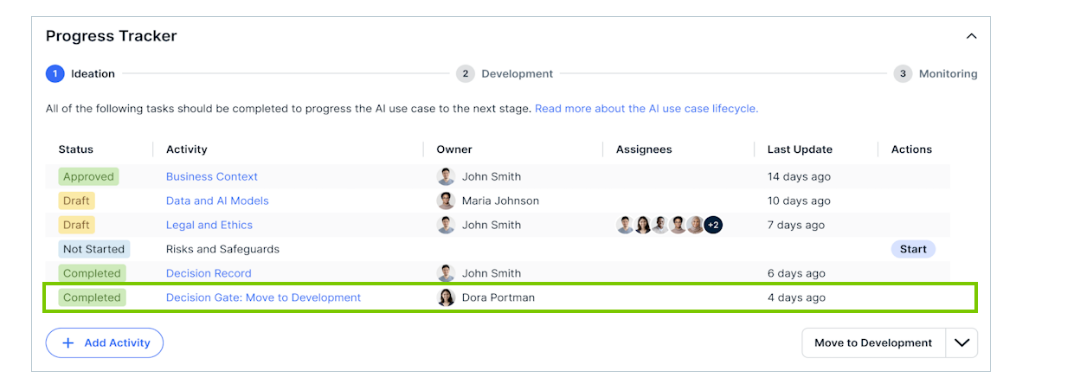
The Progress Tracker shows stakeholders and owners from various departments who are involved in use case approval.
Data (E-23 4.2): The foundation of trusted AI
Collibra promotes responsible AI by ensuring data is trustworthy. It enables documentation of data sources, quality and lineage. OSFI E-23 highlights the importance of using accurate, relevant, complete, traceable and timely data for model development.
By establishing this foundation of data quality and lineage, Collibra helps mitigate the risk of flawed decisions arising from poor data quality. The platform creates transparent connections between AI use cases, models and their underlying data, clarifying ownership and stewardship responsibilities across the enterprise.
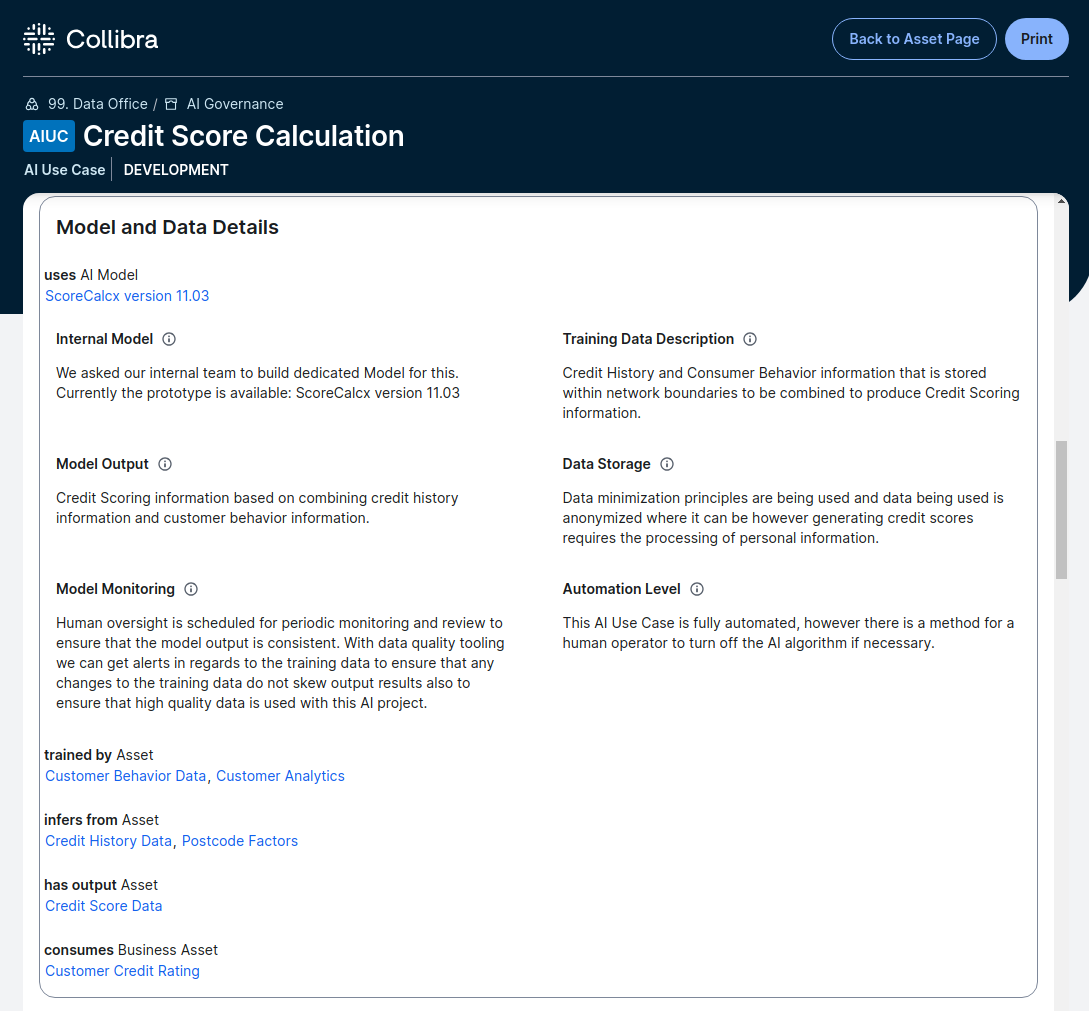
AI use cases in Collibra include business friendly descriptions of required models, inputs, training datasets, inference datasets, storage and more.
Development ( E-23 4.3): Documentation for transparency
Collibra offers tools to document the model development process, including methodology, performance metrics and outcomes. This aligns with OSFI E-23's expectation for a clear and well-documented development process.
These capabilities satisfy regulatory requirements and establish the foundation for model reproducibility and auditability that sustains AI innovation.
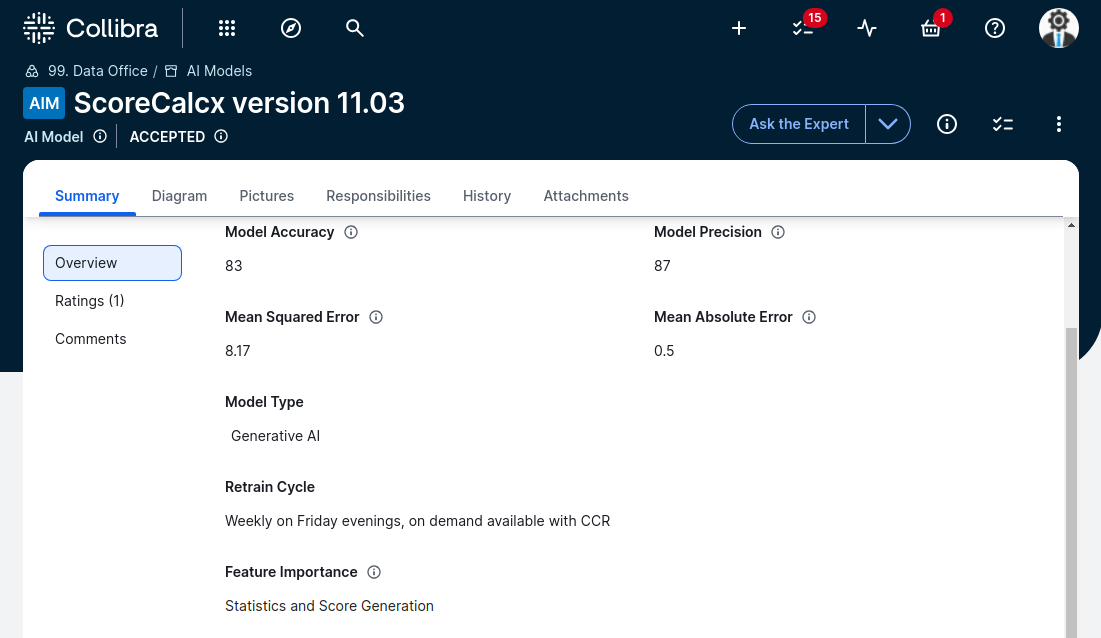
Model validation documentation can be extended and kept along with the record of the model.
Validation ( E-23 4.4): Multi-dimensional risk assessment
Collibra facilitates domain-specific assessments that evaluate AI use cases against business, data, legal and risk criteria. This aligns with OSFI E-23's requirement for independent model validation to ensure models fit their intended purpose.
Our assessment framework helps organizations identify potential issues before they surface as operational risks, strengthening validation processes while supporting regulatory compliance.
Approval ( E-23 4.5): Structured governance workflows
Collibra can help manage the model approval process. It allows for the definition of approval workflows and ensures that appropriate stakeholders review and sign off on the model before deployment. OSFI E-23 emphasizes the need for a formal approval process that considers model validation results.
Our workflow capabilities replace ad hoc approval processes with structured, auditable governance that balances innovation velocity with appropriate risk controls.
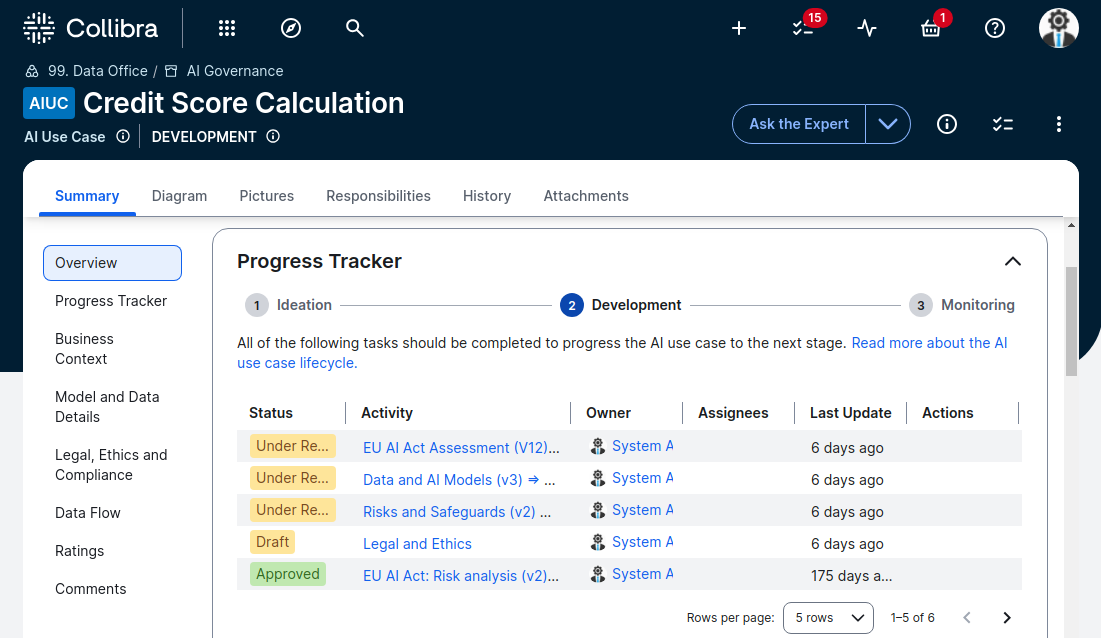
AI use cases and models are pushed through documented and auditable approval steps from ideation through decommissioning.
Deployment ( E-23 4.6), monitoring ( E-23 4.7), and decommissioning ( E-23 4.8): Full lifecycle coverage
Collibra provides comprehensive coverage across the remaining lifecycle stages:
- Deployment: Collibra integrates with AI platforms like Databricks Unity Catalog and Vertex AI. These integrations help ensure consistency between the model development and production environments, aligning with OSFI E-23's emphasis on testing models in the production environment prior to deployment
- Monitoring: Collibra assessments can be triggered periodically for models in Monitoring status to capture or validate any of the information that was created under ideation and development. Collibra allows configurability to determine what information is relevant to the monitoring of that AI use case and/or models
- Modifications and decommissioning: Collibra supports documenting modifications to AI models. Users can track changes made to the model, data sources or methodology, providing an audit trail of modifications
Building your model risk management framework
Beyond the model lifecycle, OSFI E-23 requires a comprehensive Model Risk Management Framework, another domain where Collibra delivers strategic value for:
- Model inventory
- Governance and accountability
- Risk assessment and rating
Model inventory ( E-23 5.1): The foundation of visibility
Collibra AI Governance offers a centralized repository for cataloging AI use cases. This repository can be used to create and maintain a model inventory that meets OSFI E-23 guideline. It can capture details such as model ID, version, name, risk classification, stakeholders, validation dates, performance monitoring results, dependencies and more.
This centralized inventory creates the essential foundation for enterprise-wide model risk management, providing visibility into the full AI landscape.
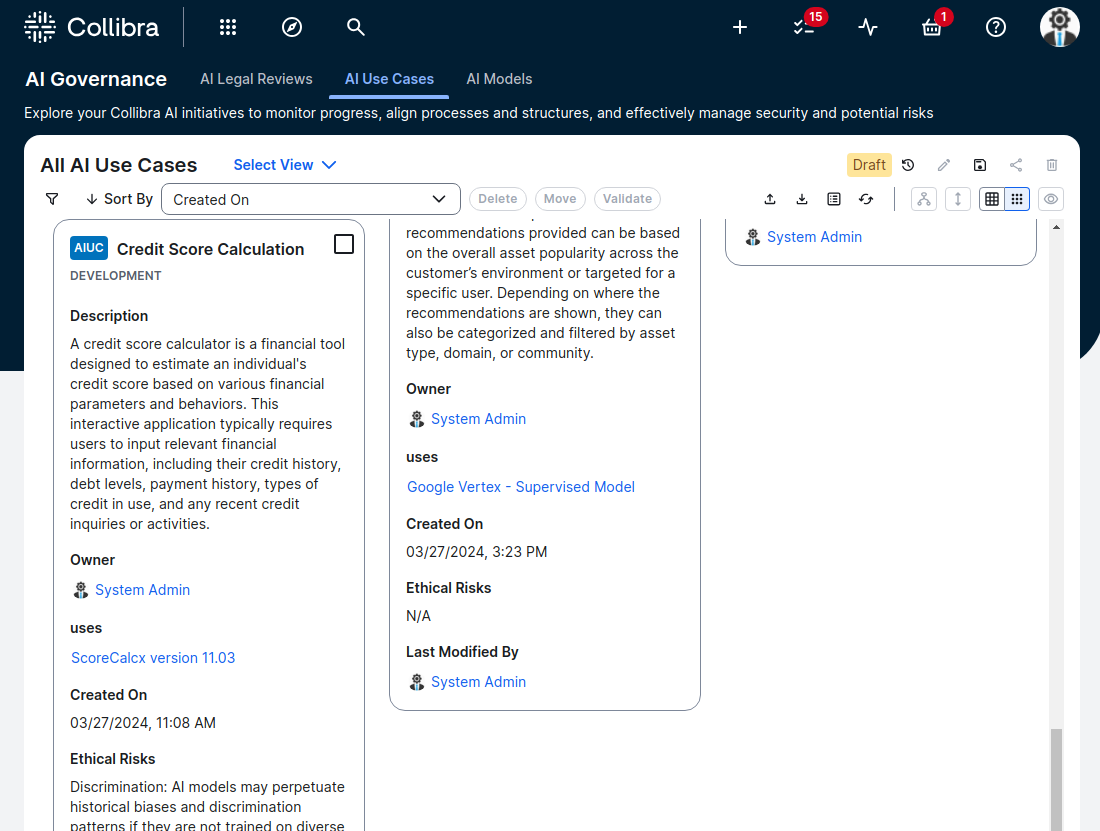
An example of an AI use case inventory.
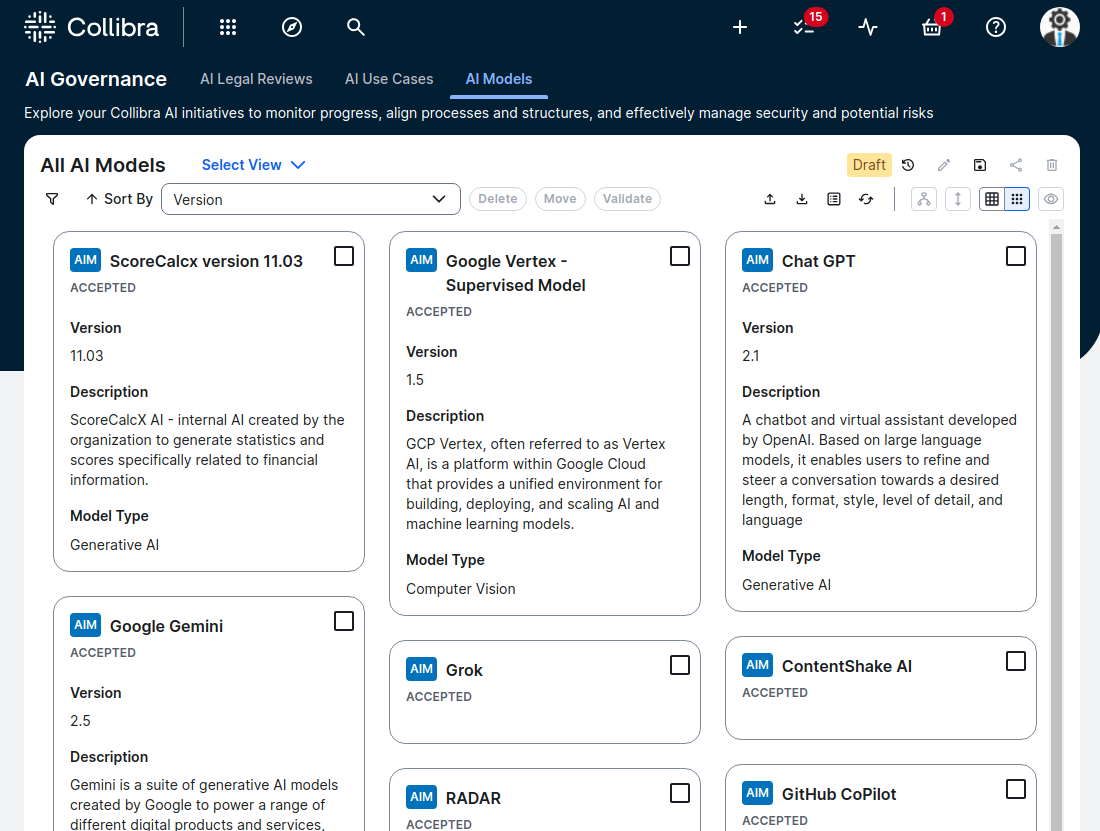
An example of model inventory.
Governance and accountability ( E-23 5.2): Orchestrating cross-functional alignment
Collibra provides features for defining roles and responsibilities, establishing governance standards, enforcing data access controls and automating workflows.
These capabilities enable organizations to:
- Define roles and responsibilities: Collibra allows assigning roles and responsibilities to individuals involved in AI projects, clarifying accountability for different aspects of the model lifecycle
- Establish governance standards: Collibra Policy Manager enables documenting and managing internal policies and regulations related to AI development and usage
- Enforce data access controls: Collibra Protect provides a no-code interface for creating and enforcing data protection policies, aligning with OSFI E-23's emphasis on protecting sensitive data
- Automate workflow processes: Collibra Workflow Engine streamlines business processes, including those related to model development, validation and approval, ensuring adherence to established procedures
Risk assessment ( E-23 5.3) and rating ( E-23 5.4): Structured evaluation framework
While Collibra AI Governance does not have a specific model risk rating system, it offers features that contribute to a comprehensive risk assessment.
These capabilities include:
- Domain-specific assessments: Collibra allows conducting assessments against business, data, legal and risk criteria, facilitating a multi-faceted evaluation of AI use cases
- Risk documentation: Collibra provides a platform for documenting known risks associated with AI use cases, including data-related risks, model limitations and potential compliance concerns
- Risk level assignment: Collibra enables assigning risk levels to AI use cases based on factors like complexity and potential impact
- Performance monitoring: Collibra's data quality and observability features allow tracking model performance and monitoring results, which can be used to inform risk assessments and reporting
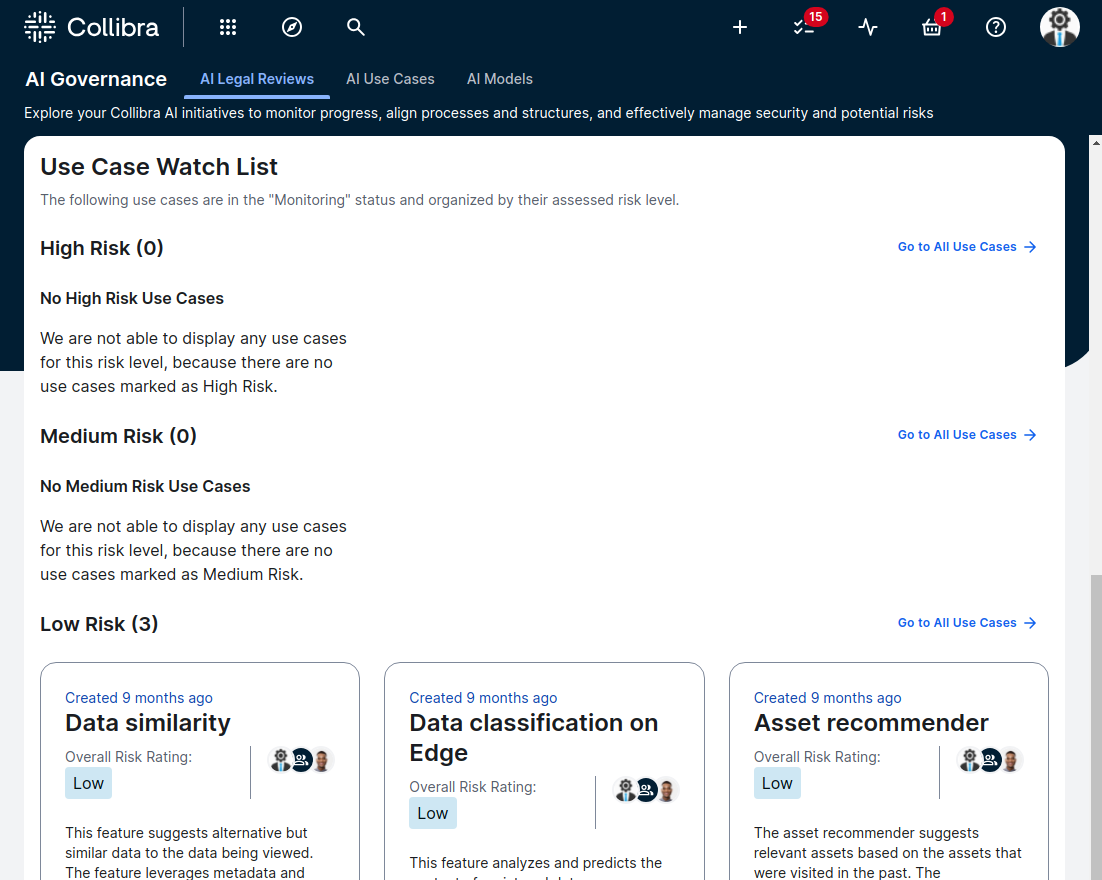
An example of a risk rating and review screen for AI use cases.
From compliance to data confidence
OSFI E-23 compliance is more than a regulatory checkbox-ticking. It's about establishing what we call "Data Confidence®."
The Collibra Platform enables organizations to trust, comply and consume all your data while the enterprise metadata graph accumulates context with every use. With Collibra AI Governance, you can establish a foundation that transforms how your organization approaches AI, leveraging the following benefits:
- Models are managed effectively throughout their lifecycle
- Risk management scales proportionally with your organization's complexity
- Models and their associated risks are clearly understood across the enterprise
Your next strategic step? Act now.
AI will make an age-old problem—not having your data house in order—untenable. Financial institutions that build a strong governance foundation today will accelerate AI initiatives tomorrow, and do it safely, confidently and with full regulatory alignment, including Canada’s OSFI E-23 regime.
Those who don't prepare now will get left behind when AI use cases and tech mature. And that’s the opportunity that presents itself now: Choosing robust controls that can actually accelerate innovation rather than constrain it.
By utilizing Collibra AI Governance for documentation, workflow automation, risk assessment and monitoring, your organizations can establish a comprehensive model risk management framework that promotes transparency, accountability and compliance. Moreover, with Collibra your institution can build trust in AI-driven operations and mitigate the potential risks associated with AI model deployment.
That's not just compliance. That's Data Confidence.
Why not begin your journey to accelerating all your data and AI use cases—without the risk—today?
Take a tour of Collibra AI Governance today.
* https://www.osfi-bsif.gc.ca/en/guidance/guidance-library/draft-guideline-e-23-model-risk-management
In this post:
- Beyond compliance: The strategic value proposition
- The governance fragmentation crisis
- The Collibra breakthrough: Unified governance
- Architecting for OSFI E-23 compliance: The Collibra framework
- Building your model risk management framework
- From compliance to data confidence
- Your next strategic step? Act now.
Related articles

AI GovernanceJune 5, 2025
Collibra + Raito: Redefining data access governance for the AI era
AI GovernanceJuly 29, 2025
Integrating Collibra with Azure AI Foundry and MLflow: New integrations expand scope of model governance

AI GovernanceJuly 2, 2025
From innovation to accountability: Collibra Azure AI Foundry Integration helps enterprises govern AI agents and models at scale—without slowing delivery
AI GovernanceOctober 6, 2025
Collibra AI agent registry: Governing autonomous AI agents
Keep up with the latest from Collibra
I would like to get updates about the latest Collibra content, events and more.
Thanks for signing up
You'll begin receiving educational materials and invitations to network with our community soon.
